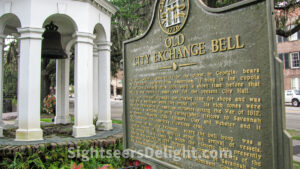Battlefield Park commemorates the Oct. 9, 1779, Battle of Savannah during the Revolutionary War. On that day, an allied force of more than 5,000 French and American troops attacked the 2,500 British soldiers defending the city. It was the second bloodiest battle of the American Revolution, and roughly 800 troops were killed or wounded during the fight. The attack failed, and allied forces retreated from Savannah on Oct. 18, 1779; the city remained under British control until 1782. The city of Savannah purchased the land in 2003, and the park built on the site includes a modern recreation of a redoubt.
The Casimir Pulaski Monument stands in Monterey Square near the battlefield where Polish nobleman Casimir Pulaski died during the siege of Savannah. Pulaski, along with Michael Kovats de Fabriczy, is considered “the father of the American cavalry.” Workers laid the cornerstone for the monument in either 1825 or 1853, depending on the source. The monument’s inscription reads, “Pulaski, the Heroic Pole, who fell mortally wounded, fighting for American Liberty at the siege of Savannah, October 9, 1779.” On October 29, 1779, Congress passed a resolution that a monument should be dedicated to Pulaski, and the Savannah monument was the first monument in the United States dedicated to Pulaski.
The Georgia State Railroad Museum is home to more than 40 railroad locomotives and cars and house in the historic Georgia State Railroad Museum roundhouse. The building dates to 1851, but the railroad demolished about half of the roundhouse in 1926 and re-engineered the facility to accommodate larger steam engines. Southern Railway, successor of the Central of Georgia Railroad, closed the facility in 1963 and subsequently started demolishing buildings on the property. The Coastal Heritage Society in 1989 took over management of the facility to preserve the shops for future generations.
31401
This dramatic bronze by sculptor James Mastin honors the Les Chasseurs-Volontaires de Saint-Domingue, the largest unit of men of African descent to fight for American independence, who took part in the 1779 Siege of Savannah. The figures include a drummer boy representing 12-year-old Henri Christophe, who would later lead Haiti and become its king. The regiment’s soldiers were free men recruited in present-day Haiti; unlike most Black combatants in the war, who joined the British after being promised freedom, these volunteers fought for the American cause. Set in Franklin Square, steps from City Market, the monument pays tribute to their courage and to Haiti’s enduring ties with Savannah. Interpretive panels provide visitors with context on the siege and the unit’s role in Savannah’s Revolutionary history today.
Savannah honors hometown legend Johnny Mercer, one of America’s greatest songwriters, with a life-size bronze unveiled on Nov. 18, 2009, the centennial of his birth. Mercer penned more than 1,500 songs across a five-decade career; “Moon River,” the theme from “Breakfast at Tiffany’s,” is his best-known classic and one of four Academy Award winners. The statue captures Mercer’s approachable charm, wearing a hat and an overcoat, a newspaper in hand, and his trademark gap-toothed grin. Set in Ellis Square, steps from City Market, it’s an easy photo stop and a fitting tribute to the Savannah native whose lyrics often echoed his love for Georgia. A restored version of the statue returned to Ellis Square in 2023.
31401
The John Wesley Monument, erected in 1969 by the John Wesley Monument Committee, honors the founder of Methodism, who served as an Anglican clergyman in colonial Georgia from 1736 to 1738. Set in the center of Reynolds Square, on the site where Wesley’s Savannah home is believed to have stood, the statue depicts him preaching outdoors, reflecting his practice of ministering in the open air, including to Native Americans, which challenged the church convention of the day. During his Savannah tenure, Wesley established what is widely regarded as America’s first Sunday school, foreshadowing Methodism’s focus on teaching and small-group faith. The bronze monument by sculptor Marshall Daugherty is located near Bay Street and City Market.
31401
This bell from the former City Exchange dates to 1802 and may be the oldest in Georgia. The bell, imported from Amsterdam, hung in the cupola of the City Exchange from 1804 until the building was razed to make way for the new Savannah City Hall built in 1905. In addition to signalling the closing time for shops, a watchman would also ring the bell in event of a fire and to welcome distinguished visitors to the city. Today, it hands in a replica of the City Exchange, which was erected in 1957.
Erected in 1858 by the U.S. Lighthouse Board, this cast-iron “street-lamp”–style beacon served as the rear range light (paired with a front light on Fig Island) to guide ships safely into Savannah Harbor and past six British vessels scuttled in 1779. The 25-foot tower (focal plane roughly 77 feet above the river) was shifted a few feet south in 1869, refurbished in 1929, and extinguished during World War II. By 1958, corrosion had necessitated the use of guy cables for stabilization. A major restoration funded with $125,000 from the Savannah Morning News and CSX dismantled, treated, repaired, and repainted the structure; it was re-erected and relit on January 11, 2001. Now within the Savannah Historic District, the beacon—originally a red light—glows today with a decorative gas lamp.
The Savannah History Museum, housed in the former Central of Georgia Depot, chronicles the history of Savannah from 1733 to modern times. Among the 40,000 artifacts housed in the museum is the bench from the movie Forrest Gump, information about Juliette Gordon Low, founder of the Girl Scouts and a steam locomotive from the early 20th century. The railroad used the building until 1972, and the Coastal Heritage Society opened the museum in 1989.
31401